ReentrantLock源码分析
ReentrantLock 定义
ReentrantLock 是 JUC 中提供的可中断, 可重入获取, 支持超时, 支持尝试获取锁
它主要有一下特点:
- 可重入, 一个线程获取独占锁后, 可多次获取, 多次释放(synchronized也一样, 只是synchronized内的代码执行异常后会自动释放到monitor上的锁)
- 支持中断(synchronized不支持)
- 支持超时机制, 支持尝试获取lock, 支持公不公平获取lock(主要区别在 判断 AQS 中的 Sync Queue 里面是否有其他线程等待获取 lock)
- 支持调用 Condition 提供的 await(释放lock, 并等待), signal(将线程节点从 Condition Queue 转移到 Sync Queue 里面)
- 在运行 synchronized 里面的代码若抛出异常, 则会自动释放监视器上的lock, 而 ReentrantLock 是需要显示的调用 unlock方法
Demo用法
1 | /** |
类结构
如下图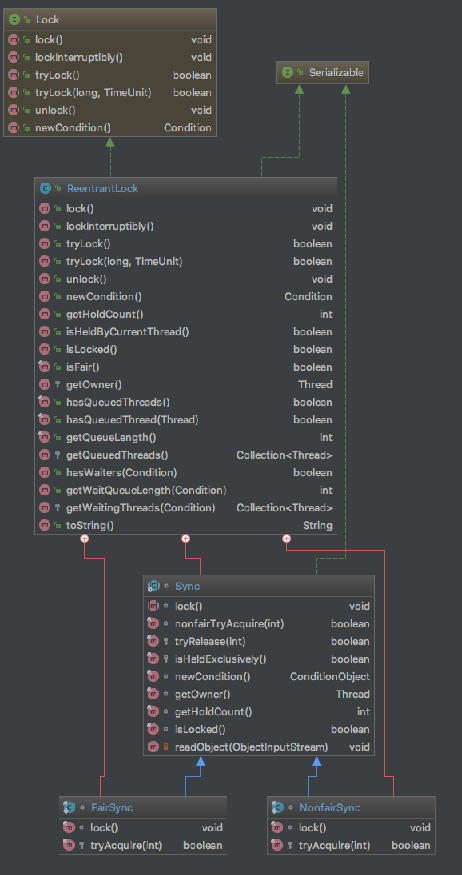
- Sync是ReentrantLock的内部抽象类,继承自AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,实现了简单的获取锁和释放锁。NonfairSync和FairSync分别表示“非公平锁”和“公平锁”,都继承于Sync,并且都是ReentrantLock的内部类。
- FairSync和NofairSync是继承Sync,公平锁和非公平锁的实现
- ReentrantLock实现了Lock接口的lock-unlock方法,根据fair参数决定使用NonfairSync还是FairSync。
源码分析
构造函数,默认是非公平锁(吞吐量大)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19/**
* 默认创建非公平锁
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
* This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.
*/
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* 通过fair来指定是否公平还是非公平
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the
* given fairness policy.
*
* @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}ReentrantLock的 lock 获取释放都是通过内部类 Sync 的子类 FairSync, NonfairSync 来实现, 而且两者都是继承 Sync, 而Sync是继承 AQS, 接下来我们看 FairSync 与 NonfairSync
ReentrantLock 内部类 FairSync 与 NonfairSync
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68/**
* 继承 Sync 实现非公平
* 公不公平的获取锁的区别:
* 1. 非公平-> 在获取时先cas改变一下 AQS 的state值, 改变成功就获取, 不然就加入到 AQS 的 Sync Queue 里面
* 2. 每次获取lock之前判断是否 AQS 里面的 Sync Queue 是否有等待获取的线程
* Sync object for non-fair locks
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
// 先cas改变一下 state 成功就表示获取
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());// 获取成功设置 exclusiveOwnerThread
else
acquire(1);// 获取不成功, 调用 AQS 的 acquire 进行获取
}
/**
* 尝试获取锁
* @param acquires
* @return
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
/**
* 继承 Sync的公平的方式获取锁
* Sync object for fair locks
*/
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
/**
* 公平的方式获取锁
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();// 1. 获取当前的 线程
int c = getState();// 2. c == 0 -> 现在还没有线程获取锁
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // 3. 判断 AQS Sync Queue 里面是否有线程等待获取 锁,若没有 直接 CAS 获取lock
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);// 4. 获取 lock 成功 设置 exclusiveOwnerThread
return true;
}
} else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 5. 已经有线程获取锁, 判断是否是当前的线程
//判断是否可重入
int nextc = c + acquires; // 6. 下面是进行lock 的重入, 就是计数器加 1
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}从代码中, 我们可以看出公平公平主要区别:
- 非公平-> 在获取时先cas改变一下 AQS 的state值, 改变成功就获取, 不然就加入到 AQS 的 Sync Queue 里面
- 每次获取lock之前判断是否 AQS 里面的 Sync Queue 是否有等待获取的线程
ReentrantLock 内部类 Sync
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83/**
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
* into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to
* represent the number of holds on the lock.
*/
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
/**
* Performs {@link Lock#lock}. The main reason for subclassing
* is to allow fast path for nonfair version.
*/
abstract void lock();
/**
* Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in
* subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
// While we must in general read state before owner,
// we don't need to do so to check if current thread is owner
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
// Methods relayed from outer class
final Thread getOwner() {
return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();
}
final int getHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;
}
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;
}
/**
* Reconstitutes the instance from a stream (that is, deserializes it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}nonfairTryAcquire, tryRelease方法都是获取 lock 的模版方法, 主逻辑在 AQS 里面, 以后会有专门的博客来分析。
ReentrantLock 获取lock方法 lock()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
//NonfairSync lock
final void lock() {
// 先cas改变一下 state 成功就表示获取
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());// 获取成功设置 exclusiveOwnerThread
else
acquire(1);// 获取不成功, 调用 AQS 的 acquire 进行获取
}
//FairSync lock 调用aqs的acquire
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}从上诉代码中我们可以看到最终都调用了AQS的 acquire 方法
ReentrantLock 响应中断的获取 lock
此方法与不响应的唯一区别时, 遇到线程中断直接抛出异常, 获取失败
也是调用了aqs的方法进行中断1
2
3
4
5
6
7/**
* 带中断的获取锁(被其他线程中断后就直接返回)
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}ReentrantLock 响应中断及超时的获取 lock
1
2
3
4
5
6
7/**
* 带中断 及 timeout 的获取锁 (线程被中断或获取超时就直接 return )
* @return
*/
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}ReentrantLock 释放 lock
1
2
3
4
5
6/**
* 释放锁
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}Condition相关,目前这边只写和reentrantlock相关部分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40/**
* 是否有线程在 Condition Queue 里面等待获取锁
*/
public boolean hasWaiters(Condition condition){
if(condition == null){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if(!(condition instanceof KAbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(" not owber ");
}
return sync.hasWaiters((KAbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);
}
/**
* Condition Queue 里面等待获取锁的长度
*/
public int getWaitQueueLength(Condition condition){
if(condition == null){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if(!(condition instanceof KAbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
}
return sync.getWaitQueueLength((KAbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);
}
/**
* Condition Queue 里面等待获取锁的线程
*/
protected Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(Condition condition){
if(condition == null){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if(!(condition instanceof KAbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
}
return sync.getWaitingThreads((KAbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);
}总结
由于ReentrantLock还涉的知识点还挺多的,考虑到篇幅问题,我们将会在接下来几篇解析Condition和AQS源码。